DeepSAT:An EDA-Driven Learning Framework for SAT
We present DeepSAT, a novel end-to-end learning framework for the Boolean satisfiability (SAT) problem. Unlike existing solutions trained on random SAT instances with relatively weak supervision, we propose applying the knowledge of the well-developed electronic design automation (EDA) field for SAT solving. Specifically, we first resort to logic synthesis algorithms to pre-process SAT instances into optimized and-inverter graphs (AIGs). By doing so, the distribution diversity among various SAT instances can be dramatically reduced, which facilitates improving the generalization capability of the learned model. Next, we regard the distribution of SAT solutions being a product of conditional Bernoulli distributions. Based on this observation, we approximate the SAT solving procedure with a conditional generative model, leveraging a novel directed acyclic graph neural network (DAGNN) with two polarity prototypes for conditional SAT modeling. To effectively train the generative model, with the help of logic simulation tools, we obtain the probabilities of nodes in the AIG being logic ‘1’ as rich supervision. We conduct comprehensive experiments on various SAT problems. Our results show that, DeepSAT achieves significant accuracy improvements over state-of-the-art learning-based SAT solutions, especially when generalized to SAT instances that are relatively large or with diverse distributions.
1. The overview of model architecture.
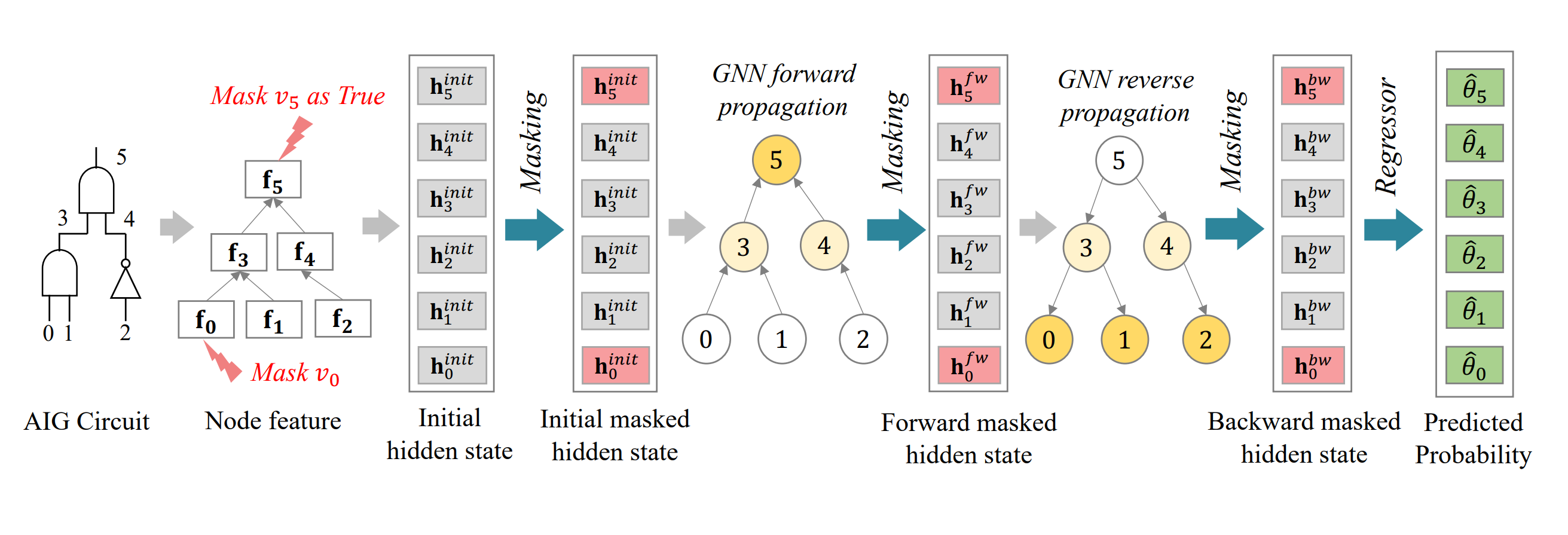
2. Pre-processing via logic synthesis.

3. Performance comparison of deepsat and neurosat on in-sample instances.
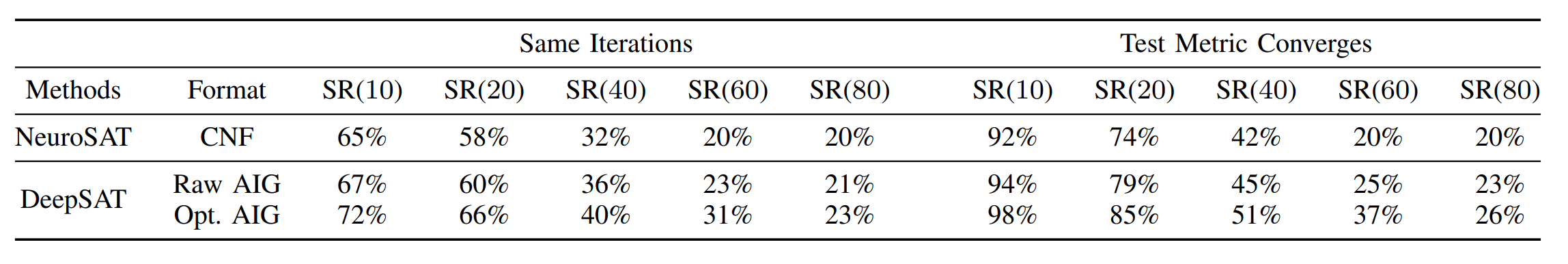
4. The comparison of deepsat and neurosat on novel distributions

@article{li2022deepsat,
title={DeepSAT: An EDA-Driven Learning Framework for SAT},
author={Li, Min and Shi, Zhengyuan and Lai, Qiuxia and Khan, Sadaf and Xu, Qiang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.13745},
year={2022}
}