Revisiting the Efficacy of Deep Active Learning for Vision Tasks
Deep Active Learning (DAL) has been advocated as a promising method to reduce labeling costs in supervised learning. However, existing evaluations of DAL methods are based on different settings, and their results are controversial. To tackle this issue, this paper comprehensively evaluates existing DAL methods in a uniform setting, including traditional fully-supervised active learning (SAL) strategies and emerging semi-supervised active learning (SSAL) techniques. We have several non-trivial findings. First, most SAL methods cannot achieve higher accuracy than random selection. Second, semi-supervised training brings significant performance improvement compared to pure SAL methods. Third, performing data selection in the SSAL setting can achieve a significant and consistent performance improvement, especially with abundant unlabeled data. Our findings produce the following guidance for practitioners: one should (i) apply SSAL early and (ii) collect more unlabeled data whenever possible, for better model performance.
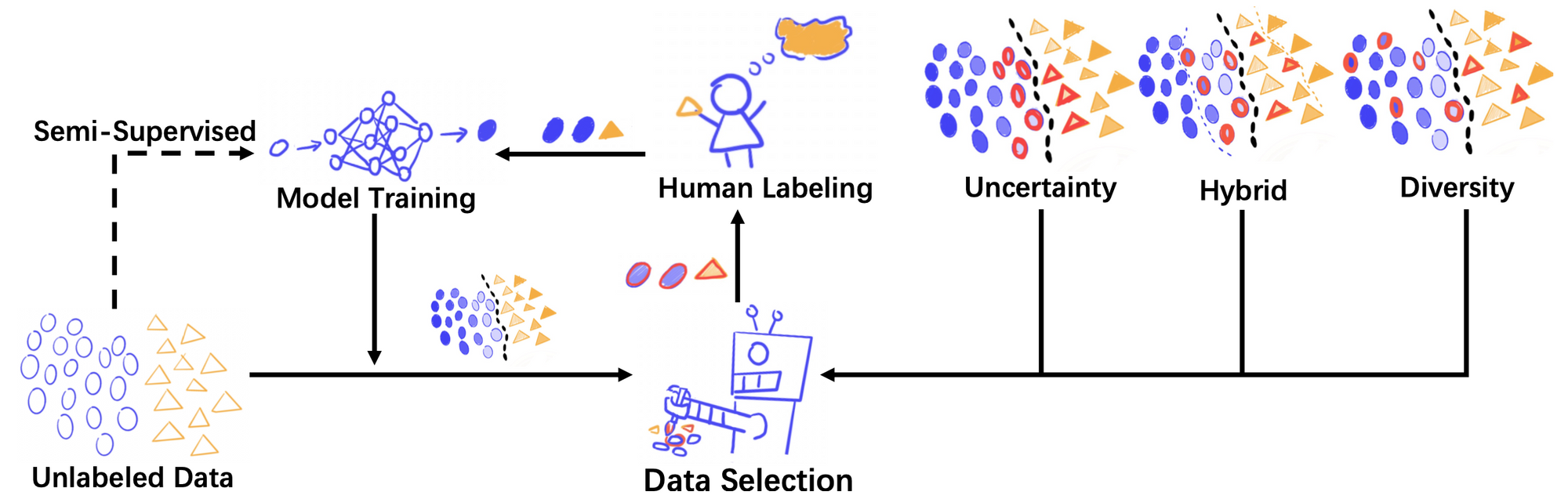
1. Deep active learning process.
2. The performance comparison of different DAL methods.

3. Comparison of different AL methods on the object detection task.

@article{li2022empirical,
title={An Empirical Study on the Efficacy of Deep Active Learning for Image Classification},
author={Li, Yu and Chen, Muxi and Liu, Yannan and He, Daojing and Xu, Qiang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.03088},
year={2022}
}