MixDefense:A Defense-in-Depth Framework for Adversarial Example Detection Based on Statistical and Semantic Analysis
Deep learning-based AI systems have dominated several long-standing machine learning tasks. Deep neural networks are increasingly used in high-stakes applications, raising worries about their safety and reliability. Fighting anomalous inputs is a major issue for safety-critical deep learning systems, and it has gotten a lot of attention from both academia and business. However, current defense/detection techniques are not satisfactory for unknown attacks or large open set applications, where the defenders have no prior knowledge of the potential attacks or open-set data distribution. This led us to explore a novel AE/OOD detection framework based on the very nature of AEs/OODs, i.e., their semantic information is inconsistent with the discriminative features extracted by the target DNN model for various anomalous inputs. This scheme allows for high detection rates with little effect on regular input accuracy.
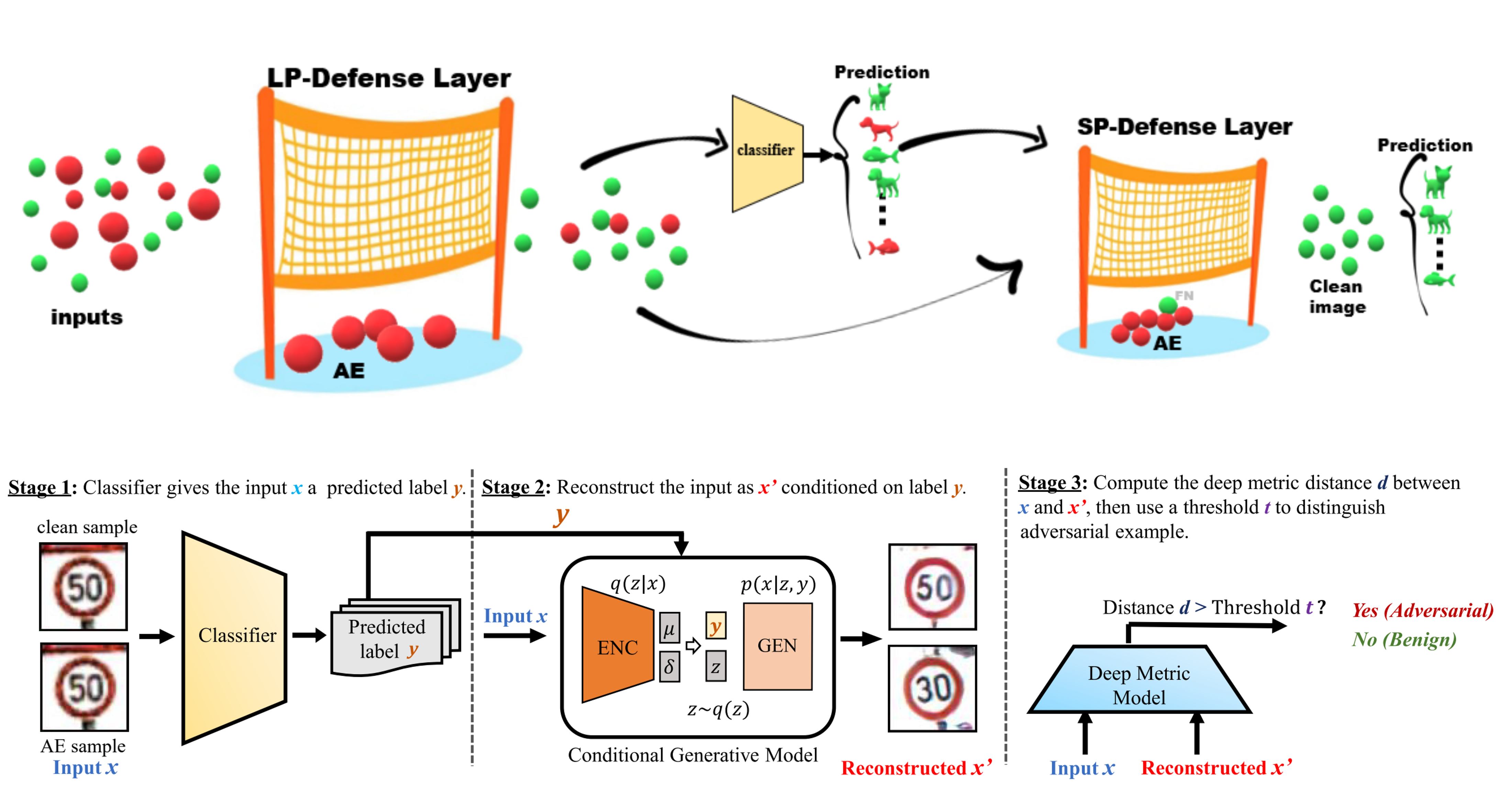
In this work, we propose a multilayer defense-in-depth framework for AE detection, namely MixDefense. For the first layer, we focus on those AEs with large perturbations. We propose to leverage the `noise’ features extracted from the inputs to discover the statistical difference between natural images and tampered ones for AE detection. For AEs with small perturbations, the inference result of such inputs would largely deviate from their semantic information. Consequently, we propose a novel learning-based solution to model such contradictions for AE detection.
@article{yang2021mixdefense,
title={MixDefense: A Defense-in-Depth Framework for Adversarial Example Detection Based on Statistical and Semantic Analysis},
author={Yang, Yijun and Gao, Ruiyuan and Li, Yu and Lai, Qiuxia and Xu, Qiang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.10076},
year={2021}
}